1. Introduction
Hoists are essential construction equipment in modern high-rise construction. Especially in the construction of high-rise and super-high-rise buildings, it plays an extremely important role. It plays an irreplaceable role in ensuring the construction period and safety, reducing construction costs, and reducing labor intensity.
At present, power frequency construction lifts still have a large market share. Although power frequency construction lifts have the characteristics of simple control circuits and simple on-site maintenance, due to the following important defects of power frequency construction lifts, they do not conform to the development rules of the industry. Sooner or later, To be replaced by variable frequency construction lifts:
a. Low working efficiency and large starting and braking impact: Power frequency elevators generally use a contactor-relay control method. The power frequency is directly started and the brake (brake) is forced to brake, which has a large impact. The magnitude of its acceleration determines The maximum operating speed generally does not exceed 33 meters/minute. Beyond this speed, people in the cage will have difficulty withstanding the acceleration during starting and braking.
b. Poor power grid adaptability: Construction sites are usually temporary power grids with long cables, and undervoltage of the grid often occurs. If the motor voltage drops by 10%, the output will drop significantly, resulting in insufficient output, failure to start, or danger due to undervoltage during operation; for a motor started at power frequency, the starting current is 5 to 7 times the rated current of the motor, further increasing the same Undervoltage risk of construction power grid.
c. The life of wearing parts is short: the two contactors in the control direction of the power frequency elevator need to carry high current to switch the drive motor. For frequently used elevators, these two contactors must be replaced within a year; because the brake (brake) ) is opened and closed during the high-speed operation of the motor, and the brake wears out quickly; because of the large impact, the life of the output gear and small roller is also very short.
2. Requirements for electronic control systems of construction elevators
Safety is the top priority of construction elevator electronic control systems. By matching the anti-fall safety device, the occurrence of cage falling accidents can be eliminated. The anti-fall safety device is an important safety component of construction lifts, and an anti-fall test must be conducted every three months. The current drop test is to increase the output frequency of the frequency converter to make the motor-driven cage run at a simulated falling speed to see whether the anti-fall safety device operates.
At present, the commonly used motor specifications used in construction elevators are 7.5 to 22kW, and construction elevators are usually equipped with 1 to 3 motors. When a construction lift is equipped with multiple motors, there are two common configurations for frequency converter selection:
1) Configure a considerable number of frequency converters according to the number of motors. The power of the frequency converter is equivalent to the power of the motor. For example, when the number of motors used in a construction lift is 2 and the power of each motor is 15kW, you can choose two 15kW or 20kW inverters. At this time, the manufacturer will require the two inverters to operate on a common DC bus.
2) Controlled by a high-power frequency converter. For example, when the number of motors is 2 and the power of each motor is 15kW, a 40kW inverter can be selected (the power of the inverter is >2×15kW×1.2, and 1.2 is the overload factor).
3. PLC frequency conversion speed control system for construction ladders
The principle of the frequency conversion speed control system of the construction ladder is shown in Figure 1. The PLC sends control instructions to the frequency converter based on the position and speed signals of the elevator, and the frequency converter controls the power system of the elevator according to the instructions. At the same time, when the frequency converter detects a fault, the frequency converter sends a signal to the PLC, and the PLC activates the protective relay according to the control instructions and cuts off the power supply, thereby protecting the hoist power system.

Figure 1
4. Introduction to FR500C frequency converter
(1)Features and advantages of FR500C on construction elevators
FR500C frequency converter is a high-performance frequency converter specially developed for lifting applications. FR500C has a unique brake control logic, which greatly improves the ride comfort of the elevator and increases the maximum operating speed of the elevator. FR500C has been successfully used on many customers' low-speed elevators (0 to 33 meters/minute) and medium-speed elevators (0 to 63 meters/minute).
FR500C can control the cage to achieve direct switching between up and down and frequent inching leveling operations, further improving the work efficiency of the construction elevator.
The FR500C product also has a wide input voltage range and can work reliably within the range of 380V±15%. Many customers have taken a fancy to this and started to use FR500C on construction lifts. FR500C solves the problem of poor power grid adaptability of power frequency elevators. In addition, FR500C controls the soft start and soft stop of the motor. The maximum grid-side starting current does not exceed the rated current of the motor, which will not cause voltage drops in the same power grid on the construction site and reduce the impact on surrounding construction equipment.
The braking unit is built-in to 90KW, and the size is also significantly reduced, which can significantly reduce the size of the electric control cabinet.
After applying FR500C, the direction control of the elevator is realized by the frequency converter, eliminating the two contactors for controlling the direction; because the frequency converter controls the opening and closing of the brake when the cage speed is almost zero, the impact is very small. The service life of the brake (brake), output gear, and small roller is greatly extended.
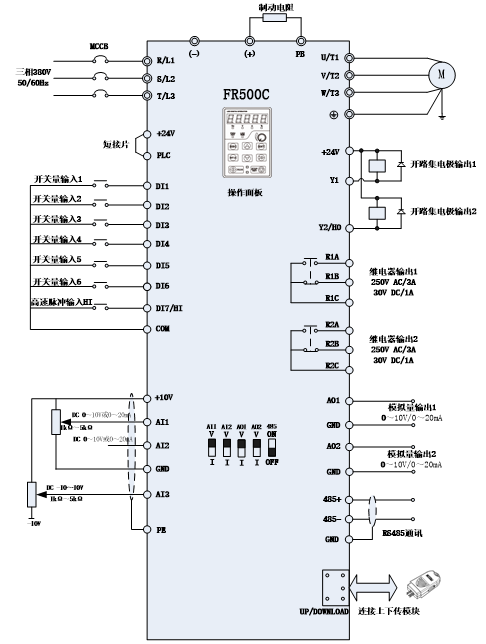
(2)FR500C wiring schematic diagram
Figure 2
Lift electrical box control diagram
(3)Quick debugging parameters of FR500C (taking 55KW as an example)
Figure 3
(4)Debugging precautions
a. After ensuring that the main circuit and control circuit wiring are correct, the system starts powering on and debugging. Set the parameters of the motor through the operation panel on the frequency converter, and select the static self-learning method to identify the motor. After the identification is completed, set the control mode, output frequency, acceleration and deceleration time, relay DO output mode, and brake release and locking detection. Frequency and other corresponding parameters (the specific setting parameters can be found in the instruction manual of each inverter). After the parameter setting is completed, in accordance with the international experimental rules for construction elevators, several stages of no-load debugging, rated load debugging and 125% rated load debugging will be carried out. . During debugging, if the hook phenomenon occurs, the brake frequency can be appropriately increased, but it should not be set too high, otherwise the inverter will easily report a fault. It is generally set within 0.3~2Hz.
b. Safety is the most important standard for hoists. Safety testing must be conducted in accordance with national standards during system debugging. During the no-load test, you can test whether the limit switches such as the upper and lower limits of the hoist and each door of the cage operate according to the design standards: After debugging at 125% of the rated load, adjust the overload protector to 110% and conduct an overload test. For the anti-fall test, an anti-fall safety device is usually installed on the hoist. The anti-fall safety device is an important component of the hoist. It must be relied on to eliminate the occurrence of cage falling accidents. The hoist used on the construction site must be installed every three months. Conduct a drop test once every month. The drop test can be done by increasing the output frequency of the inverter to make the motor-driven cage simulate a falling speed to see whether the anti-fall safety device operates.
(5)Selection of FR500C braking resistor
When the frequency converter decelerates with a large inertia load or requires rapid deceleration, the motor will be in the power generation state and transfer the load energy to the DC link of the frequency converter through the inverter bridge, causing the frequency converter bus voltage to rise. When it exceeds a certain value, the frequency converter An overvoltage fault will be reported, or even overvoltage damage to the internal power module of the frequency converter. To prevent this phenomenon, a braking component must be configured.
The following are the recommended braking resistor power and resistance values. Users can change the value appropriately according to load conditions, but it must be within the recommended range.

Figure 4
Note:The conductor should be a cable with a voltage resistance of AC450V or above and a temperature resistance of 105°C.
Taking into account the braking performance and the heat dissipation performance of the resistor in hot weather, the selection principle of the brake resistor specifications is based on two aspects: the equivalent resistance value is kept at the recommended minimum resistance value, and the power selection is more than twice the recommended power.
5.Conclusion
Applying the FR500C series frequency converter to construction elevators can achieve soft start and stop of the elevator, small impact, and good riding experience; FR500C has a built-in braking unit, which reduces the installation of external braking devices and reduces the difficulty of installation and operation; the braking is smooth and the work efficiency High, stable performance and remarkable effect.
6. Construction elevator application site pictures